SMS Envocare

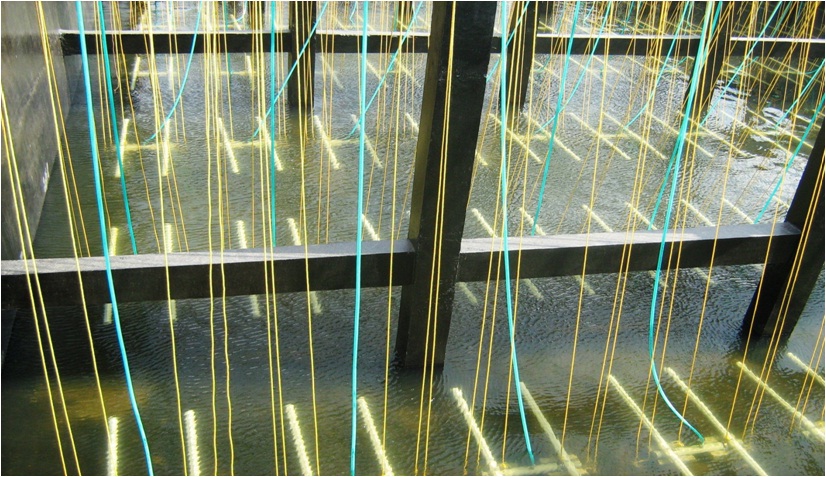
Wastewater treatment: Go for it!
May 8, 2014
Solar Power, It’s Your, It’s Free!
September 26, 2017When you think about the variety of materials that enter the wastewater system from a typical home, the list is diverse and extensive: wastes from toilets; soap, detergents, and cleaning products from drains and washing machines; food items from garbage disposals – all along with large quantities of water. How is this material removed so that the water may be safely returned to the environment and possibly utilized again by other people downstream?
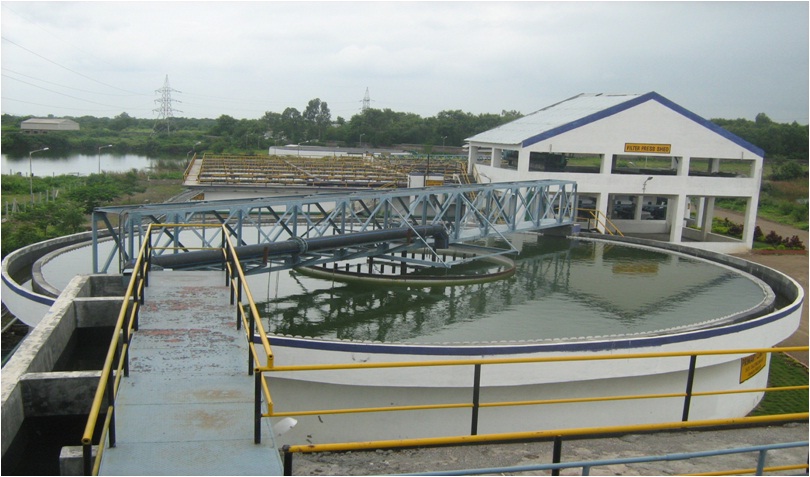
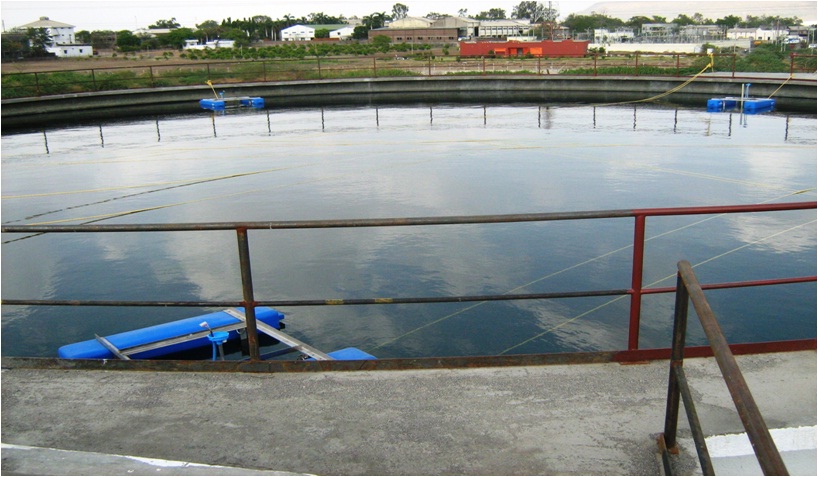
Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants from the wastewater and household sewage. It includes physical, chemical and biological process to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants. The objective of sewage treatment is to produce a disposable effluent without causing harm to the surrounding environment and prevent pollution.
Hazardous wastes pose a potential threat to the society as they are very harmful. Most of the Hazardous wastes are disposed as they can cause health issues but few wastes can be recycled. Lead-acid batteries or electronic circuit boards and convert them into easier-to- dispose solids, or they could be used as pavement filling. Such treatments reduce the level of threat of harmful chemicals.
The effluent treatment plant is designed to treat the effluent coming from different areas of the plant. The treatment of effluents varies with the type of effluents; they can be Oily Water Effluent Treatment, Service Water Effluent Treatment, and Sludge Handling System etc.
Desalting device essentially separates saline water into two streams: one with a low concentration of dissolved salts (the fresh water stream) and the other containing the remaining dissolved salts (the concentrate or brine stream). There are various desalination processes such as:
Multi Stage Flash Distillation (MSF), Multiple Effect Distillation (MED), Vapor Compression Distillation (VC), Membrane, Reverse Osmosis (RO), Electrodialysis (ED).
Medical wastes are a type of Hazardous waste and hence they should be properly managed and disposed or they can cause health threats. To protect the public and the environment from potentially infectious disease causing agent The Government of India has promulgated the Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules 1998. They are applicable to all persons who generate, collect, receive, store, transport, treat, dispose or handle biomedical wastes. This includes hospitals, nursing homes, clinics, dispensaries, veterinary institutions, animal houses, pathological laboratories and blood banks.